Mold is one of the most common household problems, but many people don’t fully understand what it is. Is mold a fungus or bacteria? The short answer is that mold is a type of fungus. However, its characteristics and behaviors make it uniquely different from bacteria. This article dives deep into the scientific differences between fungi and bacteria, how mold fits into the picture, and what you need to know to protect your home and health.
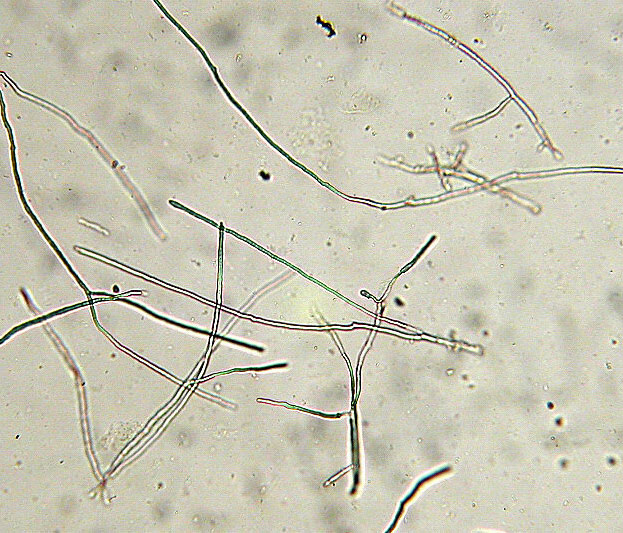
What Is Mold? A Quick Overview
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in multicellular structures called hyphae. These hyphae form visible colonies that thrive in damp, humid environments. Unlike bacteria, which are single-celled microorganisms, mold is more complex and requires specific conditions to grow and reproduce.
Mold spreads through microscopic spores that float in the air, allowing it to colonize new areas quickly. These spores can cause health problems when inhaled or when they come into contact with the skin.
Mold vs. Bacteria: Key Differences
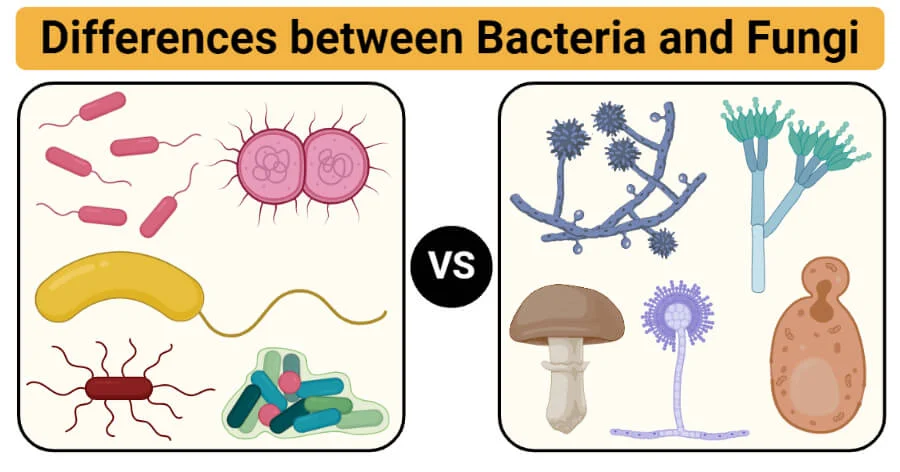
Understanding the differences between mold and bacteria is essential for managing mold effectively. Here’s a breakdown of their main characteristics:
Table: Mold vs. Bacteria
| Characteristic | Mold (Fungus) | Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Structure | Multicellular | Single-celled |
| Size | Larger, visible as colonies | Microscopic, invisible to the naked eye |
| Growth Environment | Thrives in damp, humid conditions | Can grow in a variety of conditions, including extreme heat and cold |
| Reproduction | Produces spores for reproduction | Reproduces through binary fission |
| Health Impact | Causes allergies, respiratory issues, and infections | Can cause infections, foodborne illnesses, and diseases |
Why Mold Is Classified as a Fungus
Mold is classified as a fungus because it shares the defining characteristics of fungi, including:
- Cellular Structure: Mold cells have a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes, unlike bacterial cells, which lack a nucleus.
- Growth and Reproduction: Mold grows as a network of hyphae and reproduces through spore formation, a hallmark of fungi.
- Nutrition: Mold absorbs nutrients from organic material, breaking it down with enzymes, similar to other fungi.
How Mold and Bacteria Affect Your Home and Health

While both mold and bacteria can be harmful, their effects differ significantly. Here’s how each impacts your home and health:
Impact of Mold
- Damages walls, ceilings, and furniture by breaking down organic materials.
- Causes allergic reactions, asthma attacks, and respiratory infections.
- Produces mycotoxins that can lead to long-term health problems.
Impact of Bacteria
- Contaminates food, leading to foodborne illnesses like salmonella and E. coli infections.
- Causes diseases such as strep throat, tuberculosis, and urinary tract infections.
- Can create biofilms on surfaces, making them harder to clean.
How to Identify and Manage Mold in Your Home
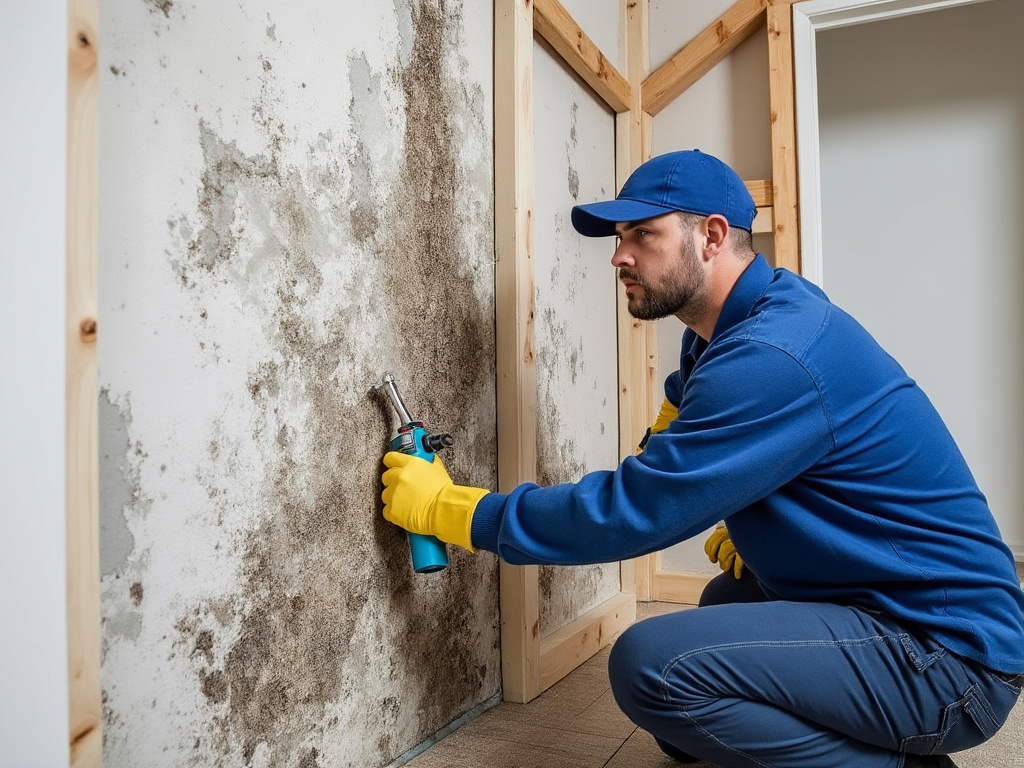

Step 1: Identify Mold
Check for the following signs of mold in your home:
- Visible Growth: Black, green, or white patches on walls, ceilings, or furniture.
- Musty Odor: A persistent, earthy smell in certain areas.
- Health Symptoms: Allergies, coughing, or skin irritation may indicate mold exposure.
Step 2: Remove Mold Safely
For small infestations, follow these steps:
- Wear protective gear, including gloves and an N95 mask.
- Scrub surfaces with a mixture of vinegar and water or a commercial mold remover.
- Dry the area thoroughly to prevent regrowth.
Warning: Large mold infestations require professional remediation. Contact Citywide Mold Mitigation for expert help.
Step 3: Prevent Mold Growth
- Fix leaks and dry wet areas immediately.
- Maintain indoor humidity below 50% with a dehumidifier.
- Ensure proper ventilation in high-moisture areas like bathrooms and kitchens.
FAQs About Mold and Bacteria
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is mold a fungus or bacteria? | Mold is a type of fungus, not bacteria. |
| Can mold and bacteria grow together? | Yes, mold and bacteria can coexist in damp, unsanitary environments. |
| Which is more dangerous, mold or bacteria? | It depends on the type and exposure. Mold can cause respiratory issues, while bacteria can lead to infections and diseases. |
| How do I test for mold? | Professional mold inspections or DIY test kits can identify mold in your home. |
| Does cleaning with bleach kill mold and bacteria? | Bleach can kill surface mold and bacteria but may not eliminate mold on porous materials. |
Conclusion: Understanding Mold for a Healthier Home
While mold and bacteria share some similarities, they are fundamentally different organisms. Mold, as a type of fungus, poses unique challenges to homeowners due to its spore-based reproduction and ability to thrive in damp conditions. By understanding the nature of mold and taking proactive steps to manage it, you can protect your home and family from its harmful effects.
For professional mold removal and prevention services, trust Citywide Mold Mitigation. Our experts are here to help you create a safe, mold-free environment.

